엔진 기술
미래에도 도로 위 자동차의 대부분은 내연기관으로 구동될 것입니다. 따라서 내연기관이 최대한의 효율성을 갖추도록 하는 것이 타당합니다.
우리는 아람코 글로벌 연구센터와 자동차 산업과의 파트너십을 통해, 내연기관을 개선하고, 전 세계 에너지 소비자를 위해 배출을 크게 저감하며 연료 효율성을 향상할 수 있는 획기적인 수송 기술을 발전시키고 있습니다.
오늘날의 엔진을 다시 생각하다
아람코는 높은 효율을 제공하면서도 배출은 줄이는 내연기관과 그 구동 연료를 개발함으로서 완전히 새로운 방식으로 배출 도전과제에 접근하고 있습니다.
최소한 2040년까지는 도로 위 자동차의 대부분이 여전히 내연기관을 사용할 것으로 예측됩니다. 따라서 아람코는 고도화된 효율적인 내연기관이 중단기적으로 이산화탄소를 저감할 수 있는 가장 효과적인 방법이라고 믿습니다.
아람코 글로벌 연구센터의 전문가와 과학자들은 자동차 산업과의 파트너십을 통해 글로벌 기후 및 모빌리티 도전과제를 동시에 해결하기 위해 노력하고 있습니다.
내연기관에는 효율성 향상과 배출저감 달성을 위해 변경할 수 있는 여러 변수가 있으며, 아람코의 다양한 수송 기술은 이러한 영역 모두에 적용됩니다.
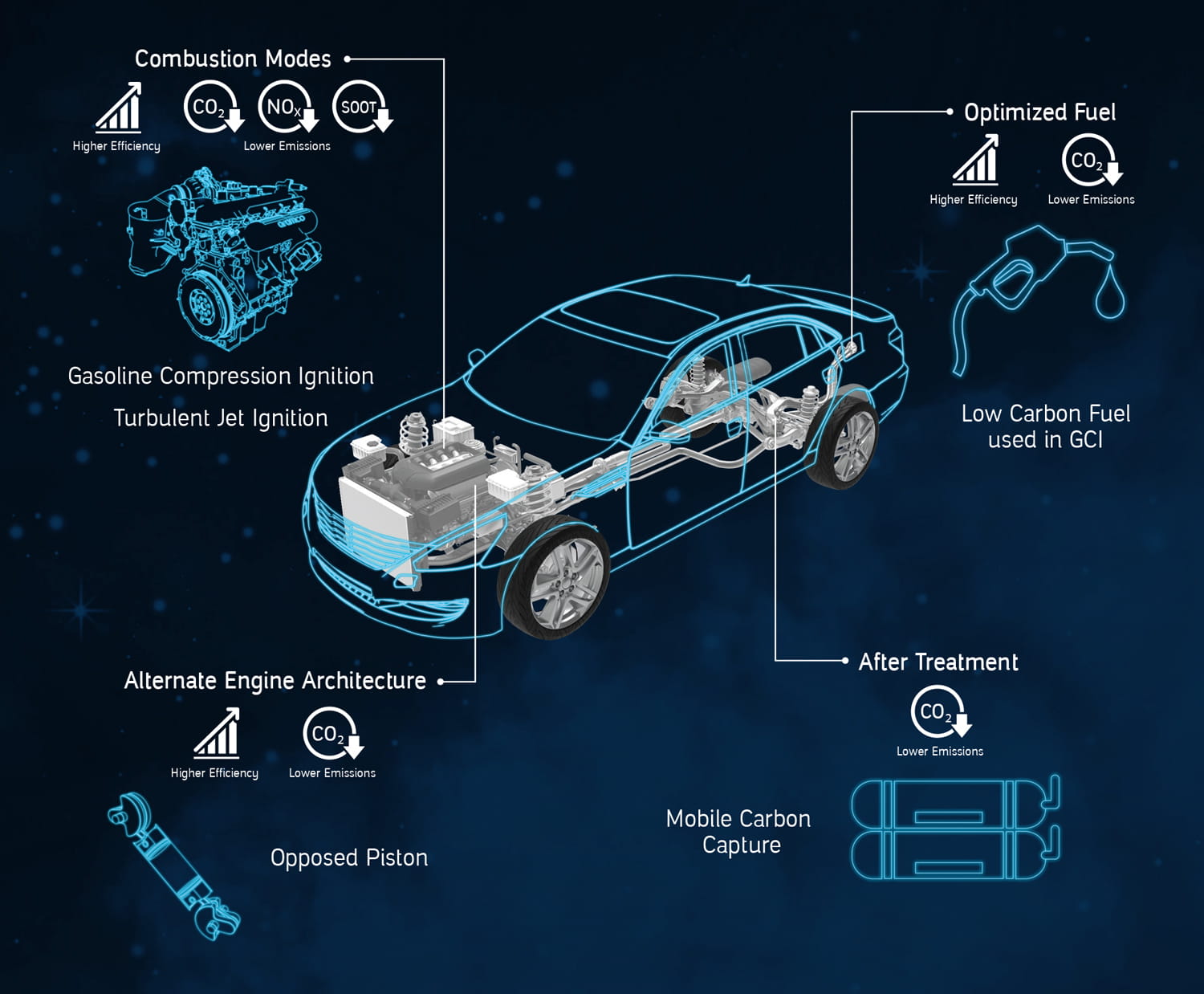
아람코는 효율성과 배출저감을 위해 차량 전반을 혁신하고 있습니다.
가솔린 압축착화
압축착화 엔진 (GCI)은 현재 사용되는 것 중 가장 효율성이 높은 내연기관입니다. 그러나 압축착화 엔진은 대부분 디젤 연료로 구동되며 상당한 양의 그을음과 질소산화물 배출을 생성하므로, 복잡한 후처리가 필요합니다.
가솔린 압축착화 엔진은 디젤만큼 즉각적으로 점화되지는 않는 가솔린 연료를 사용함으로써 연소 전에 혼합 포뮬레이션을 개선할 수 있도록 하며, 그 결과 배출을 더 쉽게 제어할 수 있습니다.
GCI는 가솔린 엔진의 효율성을 크게 향상하여 연료 소비와 이산화탄소 배출을 25% 저감합니다. 이 기술은 디젤 엔진의 효율성을 활용하면서도 엔진 배출을 매우 낮은 수준으로 낮추어줍니다.
시판 가솔린을 사용하여 실현 가능한 이러한 이점은, 최적화된 저탄소 연료를 이 기술에 사용함으로써 더욱 향상될 수 있습니다.
아람코는 이 기술을 구현하는 다양한 방법을 모색하고 있습니다. 이러한 연구 중 일부는 독립적으로 수행되며, 일부는 자동차 제조업체, 기술 개발자 및 연구기관과의 파트너십을 통해 수행됩니다. 첨단 엔진 및 연료의 공동개발을 통해 well-to-wheel에서 이산화탄소를 줄이는 것을 목표로 하는 마쓰다와의 파트너십이 하나의 예입니다.
아람코GCI 기술의 엔진 효율성 향상 이점
장점 겸비
GCI는 저배출과 저비용 고효율이라는 가솔린 엔진과 디젤 엔진이 지닌 최고의 장점을 겸비하고 있습니다.
하이브리드화
GCI의 이점은 하이브리드화를 통해 더욱 향상될 수 있습니다.
규제 이행
GCI는 자동차 제조업체의 규제 및 정책 의무 이행에 도움을 줄 것입니다.
다수의 애플리케이션
GCI는 승용차 뿐 아니라 대형 상용 트럭에서도 이점을 창출할 수 있습니다.
투자 절감
GCI는 현재의 가솔린 및 디젤 엔진 아키텍처와 주유 인프라를 활용할 수 있는 가능성을 제공함으로써, 투자를 크게 절감하고 배출저감을 가속화할 수 있습니다.
터뷸런트 제트 점화
아람코는 터뷸런트 제트 점화 (TJI)를 활용하여 가솔린 엔진을 위한 초희박 연소 전략을 개발하고 있습니다. TJI는 점화 과정을 크게 향상함으로써 연료 효율성을 개선하고 배출을 저감합니다.
이 기술은 연료와 공기의 혼합물이 또 다른 공기 또는 배기가스와 희석될 때 안정적인 방식으로 연소가 진행될 수 있도록 해줍니다.
이 기술은 주 연소실과 분리된 작은 캐비티인 프리 챔버에서 소량의 공기와 연료를 사전 혼합함으로써 작동합니다. 이후 이 혼합물이 점화되면서 주 연소실로 진입하는 고온 라디칼의 터뷸런트 제트를 생성하여, 전통적 점화 플러그보다 점화원이 더 넓게 분포하도록 합니다.
아람코는 액티브과 패시브라는 서로 다른 두 가지 접근방식에 중점을 두고 이 유망한 연소 방식에 대한 상당한 이해를 구축했습니다.
두 가지 접근방식
액티브:
스파크 플러그와 2차 연료분사기가 프리챔버 내에 설치됩니다. 이 연료분사기가 소량의 연료를 분사하고 점화 플러그가 분사된 연료를 점화하여, 연소실의 주 충전물을 점화시키는 라디칼 터뷸런트 제트를 생성합니다.
패시브:
이 접근방식은 피스톤 설계 및 분사 전략에 의존하여 소량의 공기와 연료를 프리챔버로 유도하여 점화 플러그에 의해 점화되도록 하기 때문에 2차 연료분사기가 필요하지 않습니다.
이 두 가지 접근방식은 서로 다른 하드웨어를 활용하지만, 두 방식 모두 효율성을 높이고 배출을 줄입니다.
이 기술은 여러 기술 제공업체에서 성공적으로 테스트되었으며, 아람코는 현재 2020년에 선보일 첨단 가솔린 차량에 TJI를 적용하고 있습니다. 차량 적용이 성공하면 이 기술이 가까운 시일 내에 상용화되기를 바라고 있습니다.

아람코 TJI 기술의 엔진 효율성 향상 이점
호환성
TJI는 아람코 GCI 기술이 더욱 다양한 rpm/토크 조합에서 작동하도록 하여 GCI의 이점을 확장할 수 있는 잠재력을 지니고 있습니다.
비용 효과성
하드웨어 아키텍처는 현재의 엔진 하드웨어로 구현하기에 간단하고 비용 효과적입니다.
배출저감
기존 가솔린 및 디젤 엔진에 비해 연료 효율성은 향상하고 오염물질 배출은 저감할 수 있는 잠재력이 있습니다.
규제 이행
TJI는 자동차 제조업체가 규제 및 정책 의무를 준수하도록 지원할 수 있습니다.
대향 피스톤 엔진
대향 피스톤 엔진은 큰 폭으로 향상된 출력과 효율성을 제공함으로써 유망한 대안적 아키텍처를 제시합니다.
이 엔진은 하나의 실린더에 2개의 피스톤을 사용하여 반대 방향으로 왕복 운동을 합니다. 이러한 설계는 마찰과 열 손실을 줄여 효율성을 높이고, 결과적으로 연비를 개선하고 배출을 저감합니다.
이는 다목적 솔루션입니다. 대향 피스톤 엔진은 스파크 점화 또는 압축 점화를 사용하도록 구성할 수 있고, 가솔린 또는 디젤 연료로 구동될 수 있습니다. 이러한 아키텍처를 아람코의 다른 기술과 결합하면 훨씬 더 큰 효율성 및 배출 관련 이점을 창출할 수 있습니다.
아람코는 Achates Power 및 INNEngine과 같은 타 기술 개발업체와 제휴하여, 대향 피스톤 엔진 구축을 위한 다양한 방법을 모색하고 있습니다.

Achates Power
Achates Power는 실린더와 2개의 크랭크축이 인라인으로 배열된 2행정 대향 피스톤 엔진을 개발했습니다. 아람코는 Achates Power와 제휴하여 이러한 엔진의 3기통 GCI 버전을 개발 중이며, 미래의 배출 기준을 준수하면서 차량 연비를 최대 50% 개선하는 것을 목표로 합니다.

INNEngine
INNEngine은 변속기에 토크를 전달하는 중앙 샤프트 주변에 피스톤이 배열되는 2행정 대향 피스톤 설계를 개발하고 있습니다. 이러한 배열은 엔진을 더욱 컴팩트하게 만듭니다. 이 설계는 엔진 회전당 각 실린더에 2개의 연소 이벤트를 제공하며, 이는 기존의 4행정 엔진보다 4배 높은 전력 밀도를 제공합니다. 다음 단계로 아람코는 INNEngine과 협력하여 이 기술을 더욱 발전시킬 계획입니다.
아람코 대향 피스톤 엔진의 엔진설계 개선 이점
효율성
대향 피스톤 엔진 기술은 디젤 엔진의 효율을 능가할 잠재력이 있습니다.
호환 기술
대향 피스톤 엔진 솔루션은 기존의 시판 연료와 호환 가능합니다.
저비용
대향 피스톤 엔진은 부품 수가 적어 상대적으로 복잡도가 낮습니다. 단순화된 구조에 따라 밸브 트레인과 실린더 헤드가 존재하지 않으며, 따라서 제조 비용 절감 잠재력이 있습니다.
컴팩트한 설계
컴팩트한 설계는 무게와 부피를 모두 줄여줍니다.
이동식탄소포집
이동식탄소포집 (MCC)은 수송 부문의 탄소발자국을 저감할 수 있는 혁신적인 기술입니다.
아람코 과학자들이 9년에 걸쳐 고도화한 이 기술의 가장 최근 버전은 차량 배기가스에서 배출된 이산화탄소의 최대 25%를 포집할 수 있습니다. 포집된 이산화탄소는 차량에 저장되며, 하차 후 아람코의 Converge 기술을 통해 고부가가치 제품을 만드는 것과 같이 다양한 산업 및 상업 애플리케이션으로 전환하여 활용될 수 있습니다.
아람코는 포드 F-250 픽업트럭과 중형 토요타 캠리 승용차에서 MCC 기술을 성공적으로 시연했습니다. 최근에는 이 기술을 클래스 8 대형트럭에 적용하기 시작했습니다. MCC를 GCI 및 그 외 효율성 향상 기술과 결합하여 트럭의 탄소발자국을 50% 저감하는 것을 목표로 하고 있습니다.
MCC는 화물운송과 관련된 배출을 상당히 저감할 수 있는 잠재력을 지니고 있으며, 기업 보유차량에 적용되는 경우 특히 실현 가능성이 높습니다.
이동식탄소포집 진행 상황
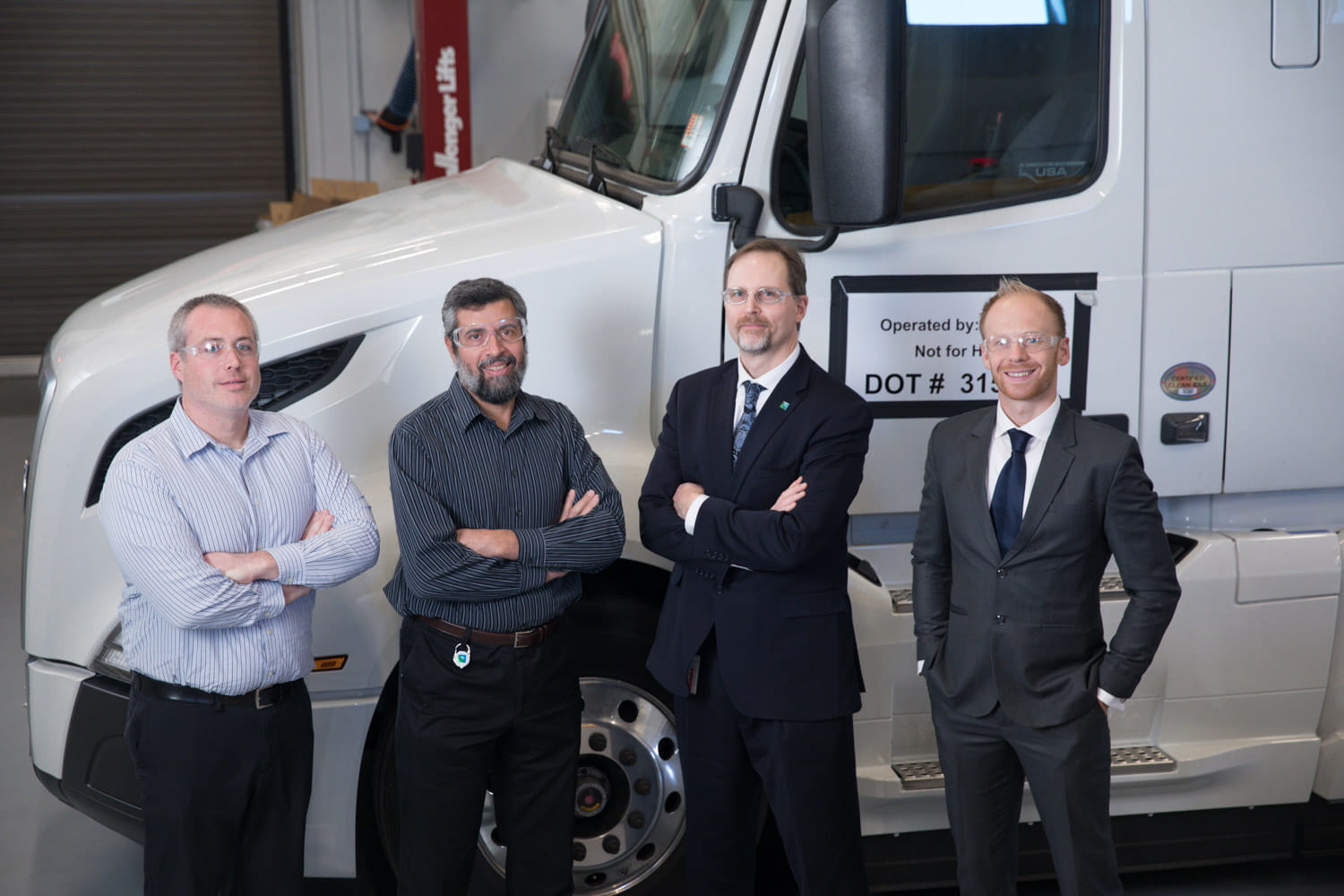

클래스 8 볼보 대형트럭을 대상으로 한 다음 시연에서 이산화탄소 50% 저감 목표
아람코 MCC 기술의 이점
50%
아람코는 MCC 기술을 통한 이산화탄소 50% 저감을 목표합니다.
화물운송 배출
MCC는 화물운송과 관련된 배출을 큰 폭으로 저감할 수 있는 잠재력을 지니고 있습니다
이산화탄소 저감
MCC 기술은 추가적 이산화탄소 저감을 위해 다른 기술들과 함께 활용될 수 있습니다.

