
탄소순환경제
이산화탄소는 지구상에서 섬세한 생명 유지 기능을 수행하지만, 수십 년간 지속된 산업화로 인해 과도한 양의 이산화탄소가 대기 중에 배출되었습니다. 탄소순환경제는 전 세계의 과도한 이산화탄소 배출을 관리하는 전 지구적 노력을 채택하기 위해 중요한 개념입니다.
탄소순환경제란?
대부분의 경제에서 상당량의 물질이 한번 사용된 후 폐기물로 버려집니다.
순환경제시스템은 이러한 자원의 재사용을 중심으로 구축됩니다. 이는 세계의 과잉 탄소를 통합하기 위해 쉽게 적용할 수 있는 모델입니다.
탄소순환경제는 탄소 배출 관리와 저감을 위한 프레임워크이며, 4R(감축, 재사용, 재활용, 제거)을 포함하는 폐쇄 루프(closed loop) 시스템입니다.
아람코는 탄소발자국을 줄이기 위한 방법으로 탄소순환경제 프레임워크를 채택했습니다.
4R
감축
재생에너지, 수력, 원자력, 바이오에너지와 같은 저탄소 에너지원의 지속적 개발과 마찬가지로, 에너지 효율성과 플레어링 최소화 역시 기후 변화 완화를 위한 중요한 조치입니다.
재사용
이산화탄소는 가치를 지닌 물질이며, 혁신적인 기술을 통한 이산화탄소 포집은 이산화탄소가 연료, 바이오에너지, 화학 제품, 건축 자재, 식음료와 같은 유용한 제품으로 재사용될 수 있음을 의미합니다.
재활용
이산화탄소는 비료나 시멘트와 같은 새로운 제품 또는 합성연료와 같은 다른 에너지 형태로 화학적으로 전환됩니다.
제거
기술을 활용하여 이산화탄소를 포집하고 저장하는 것은 배출을 대규모로 감축할 수 있 중요한 방법이며, 식물을 심어 광합성을 높이는 것도 탄소배출 저감에 기여합니다.
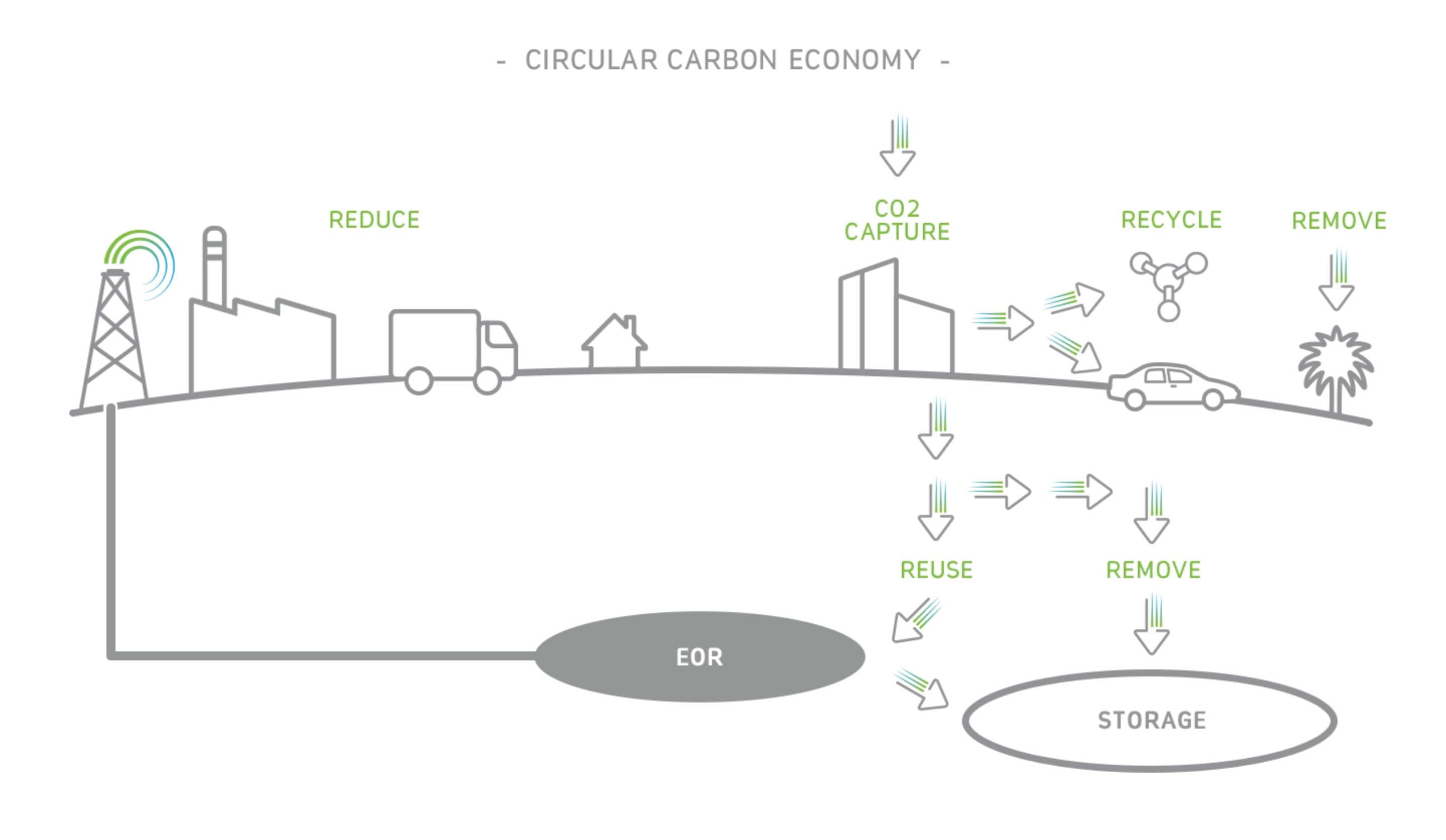
탄소순환경제는 감축, 재사용, 재활용, 제거를 통해 선형경제에서 순환경제 모델로 전환합니다.
아람코는 어떤 노력을 하고 있나요?
아람코는 탄소순환경제야말로 지속적인 경제적 성장을 보장하면서 글로벌 배출을 감축할 수 있는 최고의 프레임워크라고 믿습니다.
아람코는 다수의 탄소순환경제 이니셔티브를 실행하고 있습니다.
이산화탄소 배출을 줄이고, 연료 효율성을 높이며, 보다 친환경적인 소비재 생산을 위한 차세대 소재를 개발하고자 합니다.
아람코는 회사 활동에서 발생하는 탄소 배출의 저감을 지원할 수 있는 더 효과적인 탄소관리 솔루션을 지속적으로 혁신하고 탐구합니다.

감축: 가스 플레어링 최소화
아람코는 이러한 노력을 멈추지 않을 것입니다.

재사용: 이산화탄소 사용 및 격리
저류층에 이산화탄소를 주입하면 석유 회수를 증진하고 개선하는 동시에 이산화탄소를 격리할 수 있어, 모두에게 윈윈이 됩니다.
아람코는 사우디아라비아에서 대규모 석유회수증진 실증 프로젝트를 운영하고 있습니다. 아람코 NGL 플랜트 중 한 곳에서 이산화탄소를 포집한 후, 85km 떨어진 곳까지 파이프를 연결하여 생산량이 감소하기 시작한 성숙 유전중 한 곳에 주입합니다.
이는 수공법(waterflooding) 이후 잔류되어 있는 석유를 채굴하는 데 도움이 되며, 이 과정을 석유회수증진이라고 합니다. 이 과정에서 일부 이산화탄소는 저류층에 격리됩니다.

재활용: 새로운 소재로의 전환
탄소는 일단 포집되면 그 자체로 유용하고 가치 있는 물질로 활용될 수 있습니다.
이산화탄소는 이미 농업 등 여러 산업 분야에서 활용되고 있으며, 매일 더 많은 활용법이 개발되고 있습니다.
아람코가 추구하는 응용분야에는 더 내구성이 높고 건조가 빠른 시멘트, 탄소 섬유, 합성 연료 생산 등이 포함됩니다.
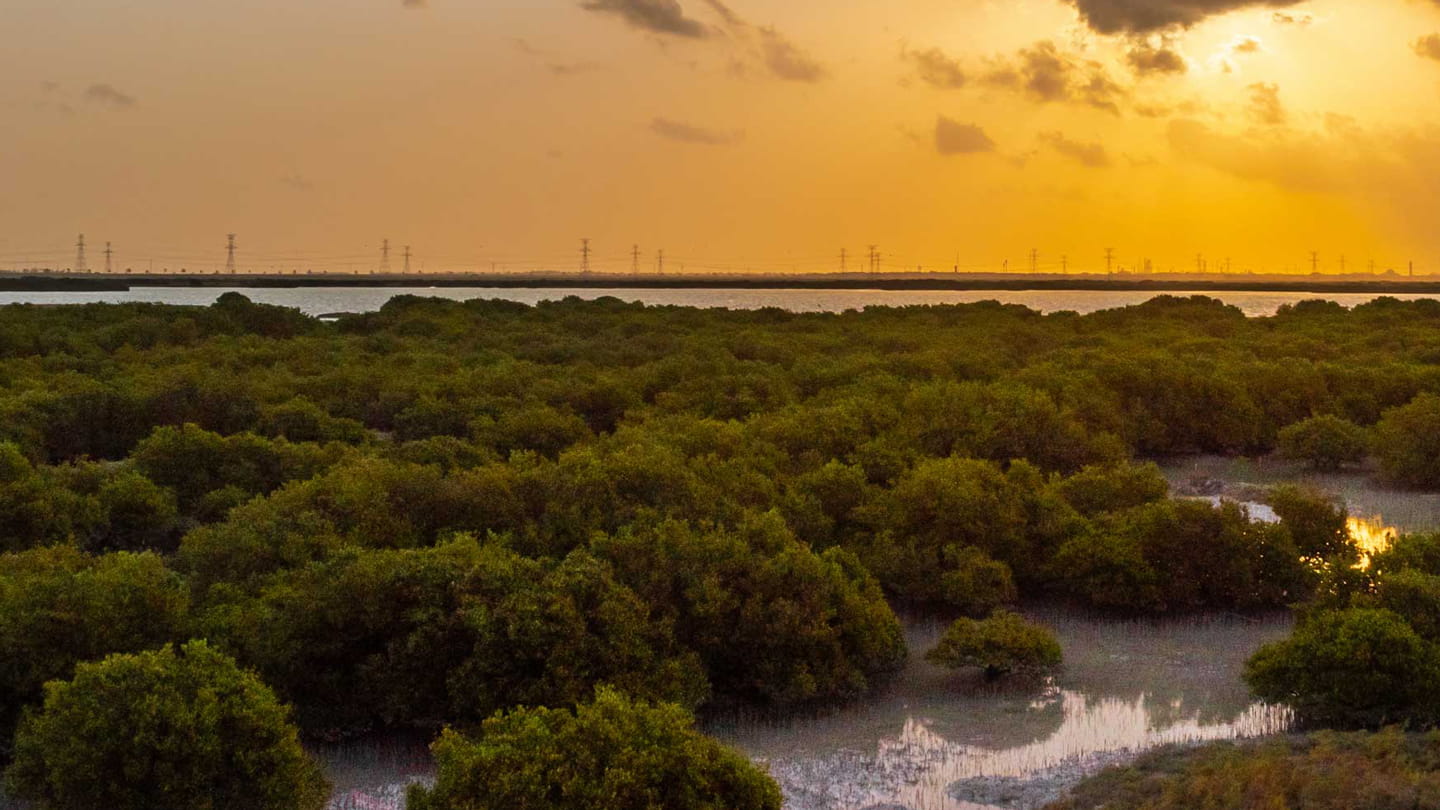

제거: 이산화탄소 포집
지금까지 아람코는 아라비아만과 홍해 연안 지역에 3000만 그루가 넘는 맹그로브 나무와 400만 그루 이상의 토종 육상 수종도 심었습니다. 또한 앞으로 수백만 그루를 더 심을 계획입니다.
맹그로브는 생물다양성을 촉진하고 해안 침식을 막는 천연 장벽 역할을 하는 서식지를 복원할 뿐 아니라, 이산화탄소의 자연 흡수원 역할을 합니다.
아람코의 이동식탄소포집 기술은 배기가스 배출을 방지함으로써 차량 이산화탄소 배출을 최대 40% 감축할 수 있는 잠재력이 있으며, 해운업계의 배출 저감을 돕는 데 유망한 것으로 입증되었습니다.
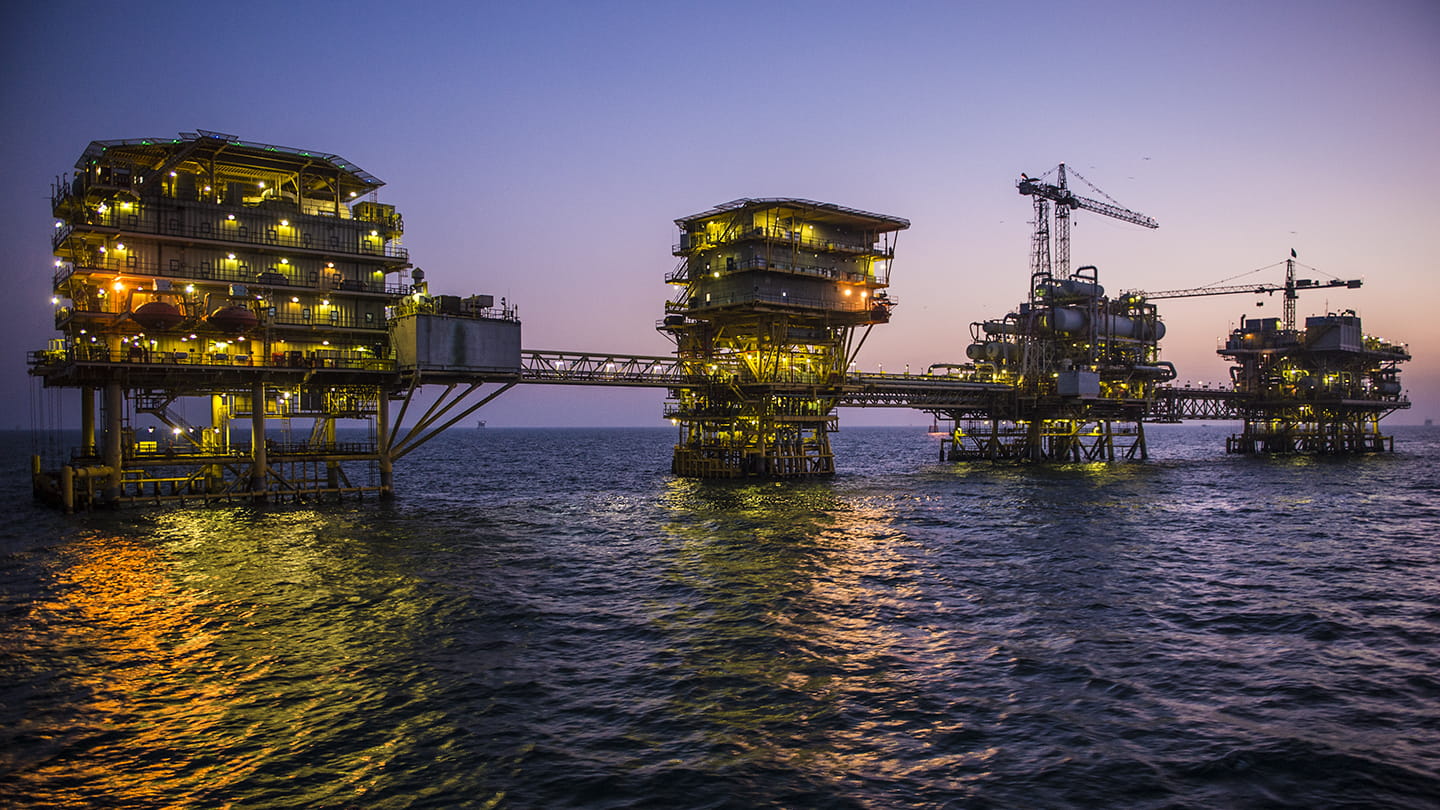


탄소 포집 & 저장
아람코는 지속가능한 에너지 미래를 보장하기 위해 전념하고 있습니다. 아람코는 탄소포집 및 저장이 전 세계의 지속가능한 번영을 보장하면서 배출을 저감하기 위한 핵심적인 역할을 수행할 것이라고 믿습니다.