대담한 디지털 신세계
인공지능에서 가상현실 프로그램에 이르기까지 사우디 아람코는 사업 운영 방식 혁신을 위해 기술의 미래에 주목하고 있다.
-
사우디 아람코는 디지털화를 통해 운영 방식을 혁신하고 있다.
-
디지털화는 지속가능성, 효율성 및 안전성을 향상할 수 있다.
-
사우디 아람코 4차 산업혁명센터 (4IR Center)는 혁신을 기술과 결합시킨다.
웨어러블 기술, 머신러닝, 석유 시추선에서의 실제 경험을 시뮬레이션하는 가상현실 프로그램은 세계적 디지털 에너지 선도기업을 향해 나아가는 사우디 아람코가 활용하는 기술 중 일부이다.
그러나 사우디 아람코에 디지털화란 단순한 기계장치 이상이다. 혁신적인 기술을 활용하여 지속가능성과 효율성, 안전성을 향상할 수 있는 기회이자, 탄화수소 자원의 환경 영향을 감소하면서 전 세계의 에너지 수요를 충족하는 사우디 아람코의 능력을 혁신하는 것을 의미한다. 사우디 아람코는 다양한 이니셔티브를 통해 이미 업계의 선도 기업들 중 최저 수준의 탄소발자국을 기록했다. 그리고 모든 사항을 고려할 때 모든 면에서 디지털화된 미래가 시작될 것으로 전망되며, 사우디 아람코는 그 길을 선도하고자 한다.
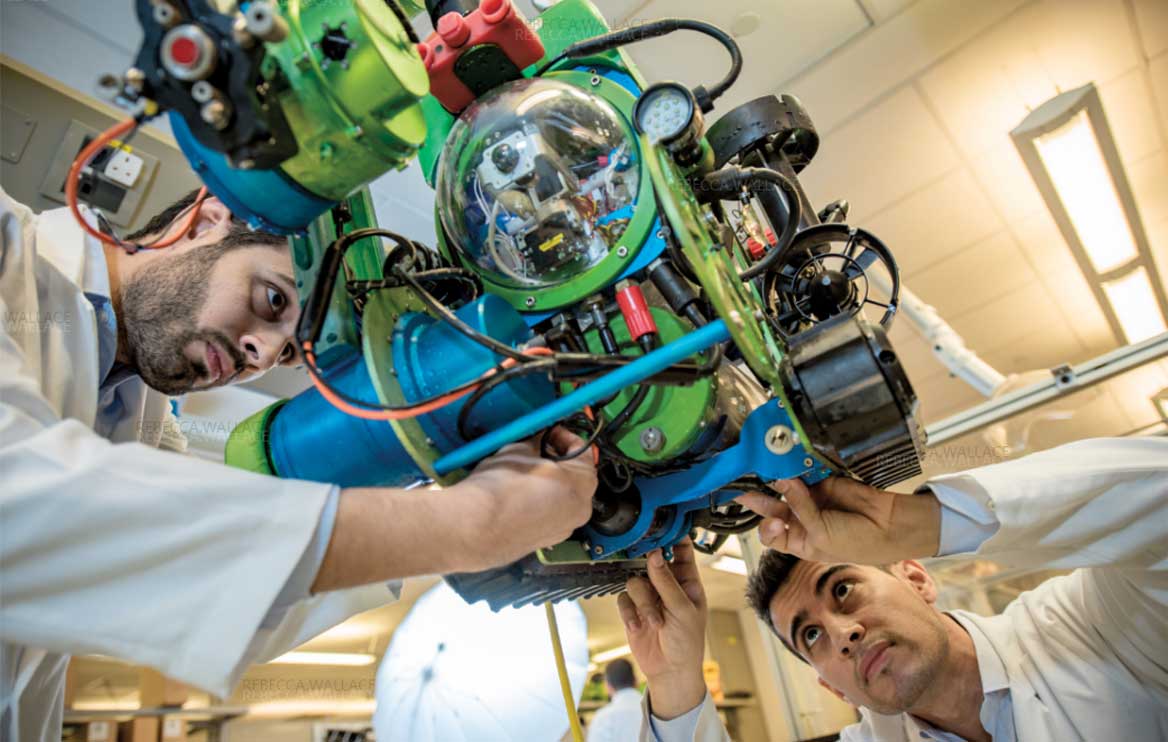
디지털 혁명
오늘날 세계에는 4차 산업혁명이 진행되고 있다. 우리 모두가 물리적·디지털·생물학적 영역 사이의 경계를 모호하게 만드는 전례 없는 빠른 기술 발전의 파도를 경험하고 있다. 핀테크, 인공지능, 사물인터넷, 블록체인, 양자 컴퓨팅과 같은 기술이 우리 삶에서 되돌릴 수 없을 정도로 깊이 자리잡게됨에 따라, 거의 모든 분야에서 큰 변화로 인한 파괴적 혁신이 초래될 것이라는 말은 과장이 아니다.
석유·가스 부문도 다르지 않다. 사실 석유·가스 부문은 업무 현장 혁신이라는 측면에서 오랫동안 가장 최첨단에 있는 산업 중 하나이다. 원격으로 작동되는 무인 시추선, 누출을 감지 할 수 있는 드론, 수중 로봇 및 지하 4D 모델링에 이르기까지 4차 산업혁명 기술의 적용은 가치사슬 전반에 걸쳐 새로운 자원과 효율성을 창출했다.
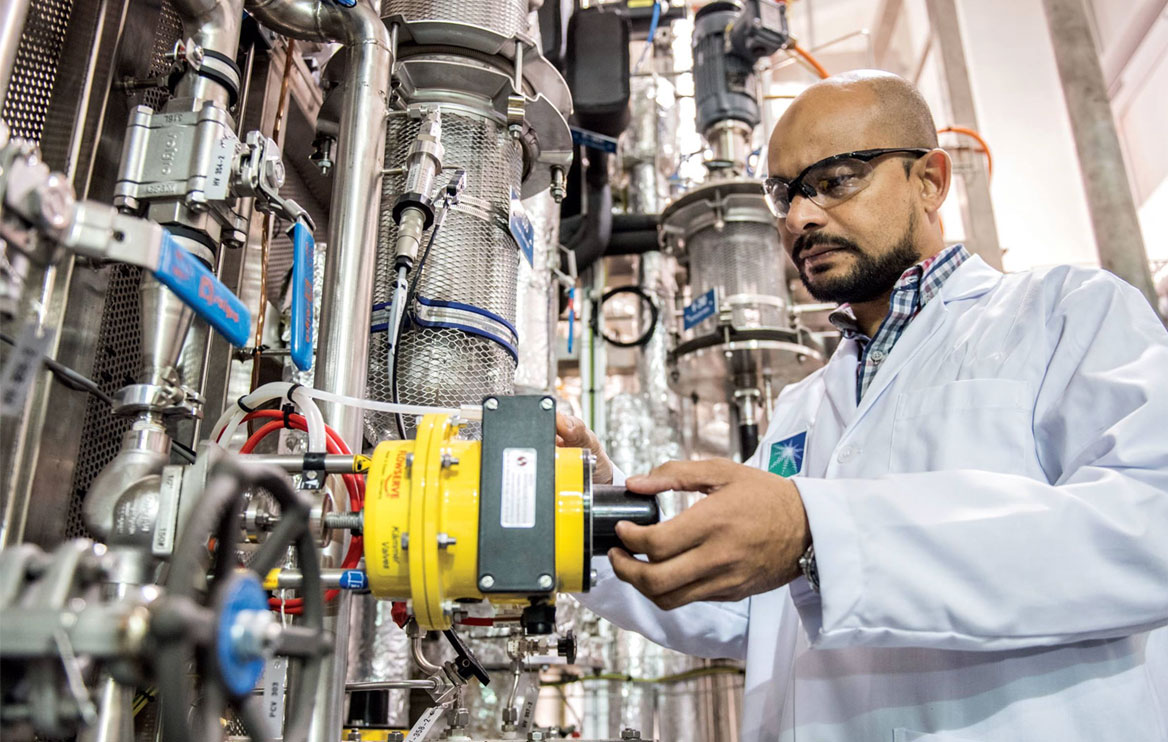

지속가능한 혁명
흥미로운 사실은 과거의 산업혁명과 달리 4차 산업혁명에서는 처음부터 지속가능성이 미래 혁신의 목표가 될 수 있다는 점이다. 사우디 아람코는 대기 중의 탄소를 포집 및 격리하고, 이산화탄소를 가치 있는 제품으로 전환하며, 수송 부문의 배출을 저감할 수 있는 획기적인 솔루션을 발전시키고, 원유를 직접 화학제품 또는 미래에 가장 선호되는 에너지인 수소로 전환하는 기술을 탐구 중이다.
세계 최대의 종합 석유·가스 기업인 사우디 아람코의 장기적 비전에는 지속가능성이 포함되어 있다. 에너지 수요가 지속적으로 증가하는 환경에서 사우디 아람코는 효율성과 경쟁력을 유지하고, 사업 활동의 환경 영향을 최소화하면서 내일의 에너지를 제공하고자 한다. 이러한 비전의 핵심은 유전에서 사무실에 이르기까지의 우리의 사업 활동에 디지털 기술들을 적절하게 통합하는 것이다.
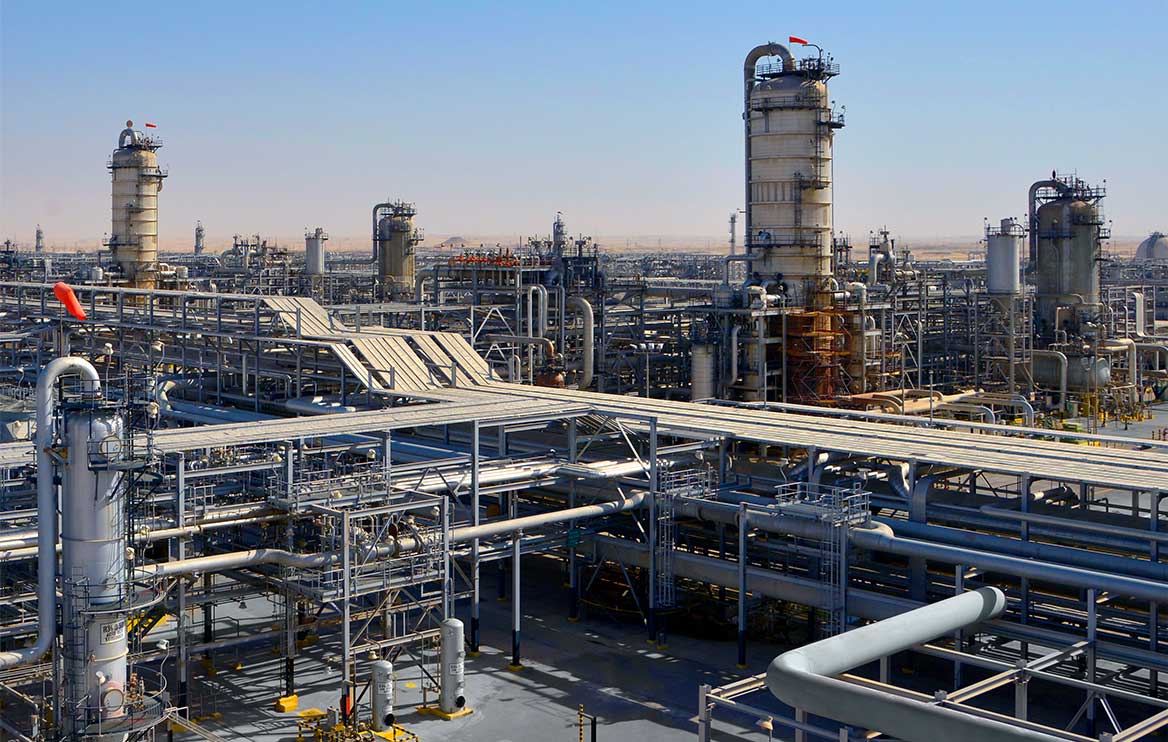

세계경제포럼의 “등대”
우스마니아 가스 플랜트를 예로 들 수 있다. 이 플랜트는 세계경제포럼 '등대 공장 프로그램 (Manufacturing Lighthouse Program)'에서4차 산업혁명에서 수행한 선도적 역할을 인정 받았다. 석유·가스 산업의 플랜트 중 최초로 세계경제포럼의 인정을 받은 것이며, 보다 효율적이고 안전하며 환경친화적인 작동방식으로 찬사를 받았다.
사우디 아람코에서 적용 중인 기술의 예:
로봇공학 및 무인항공기 (UAV)
비상대응, 점검, 실시간 데이터 접근에 비행 로봇 (UAV), 수중 로봇 (ROV) 및 지상 로봇 (crawler)을 활용하여 진단을 개선하고 안전성을 강화하며 유지보수 비용을 절감한다.
웨어러블 기술
사우디 아람코의 현장 테크니션은 디지털 헬멧 (Digital Helmet)을 활용하여 정보를 제공하고 실시간으로 통신 및 협업할 수 있다. 테크니션은 실시간 방송을 통해 자신의 현재 시점을 그대로 엔지니어에게 전달할 수 있고, 엔지니어는 증강현실 기술을 이용하여 테크니션에게 안전하게 지침을 제공할 수 있다.
자산 성과 관리
운영 자산의 신뢰성과 안전성을 개선할 수 있도록 보건, 신뢰성, 무결성, 전략, 안전성 등 물리적 플랜트 자산을 관리하는 기술
어드밴스드 애널리틱스
예측 분석을 기반으로 자산 데이터에 발생하는 이상을 능동적으로 탐지하는 알고리즘을 적용하여, 성과 저하를 탐지하고 사용자들에게 문제의 가능성을 알린다.
스마트 플랜트, 스마트 시티
이러한 선구적인 4차 산업혁명 기술을 가능케 한 것은 디지털 혁신 프로그램이었다. 이 프로그램을 통해 사우디 아람코는 사업 전반에 최첨단 디지털 기술을 적용하여 운영 방식을 혁신한다.
예를 들어, 업스트림 부문에서는 사우디 아람코 지구과학자들이 인공지능을 활용하여 지진 데이터를 분석하고 시추 위험을 최소화할 수 있는 최적의 지점을 찾아낸다. 유전 알고리즘을 사용하여 암석을 이해하고 분류함으로써 불확실성을 줄이고, 더 효율적이고 정확하게 저류층의 특성을 파악할 수 있다. 그리고 다수의 수중 자율주행 로봇의 데이터 수집 능력을 활용하는 스파이스랙 (SpiceRack) 시스템은 특히 까다로운 수중 위치에서 데이터를 수집하여 탄성파 데이터 수집 산업에 혁명을 일으켰다.
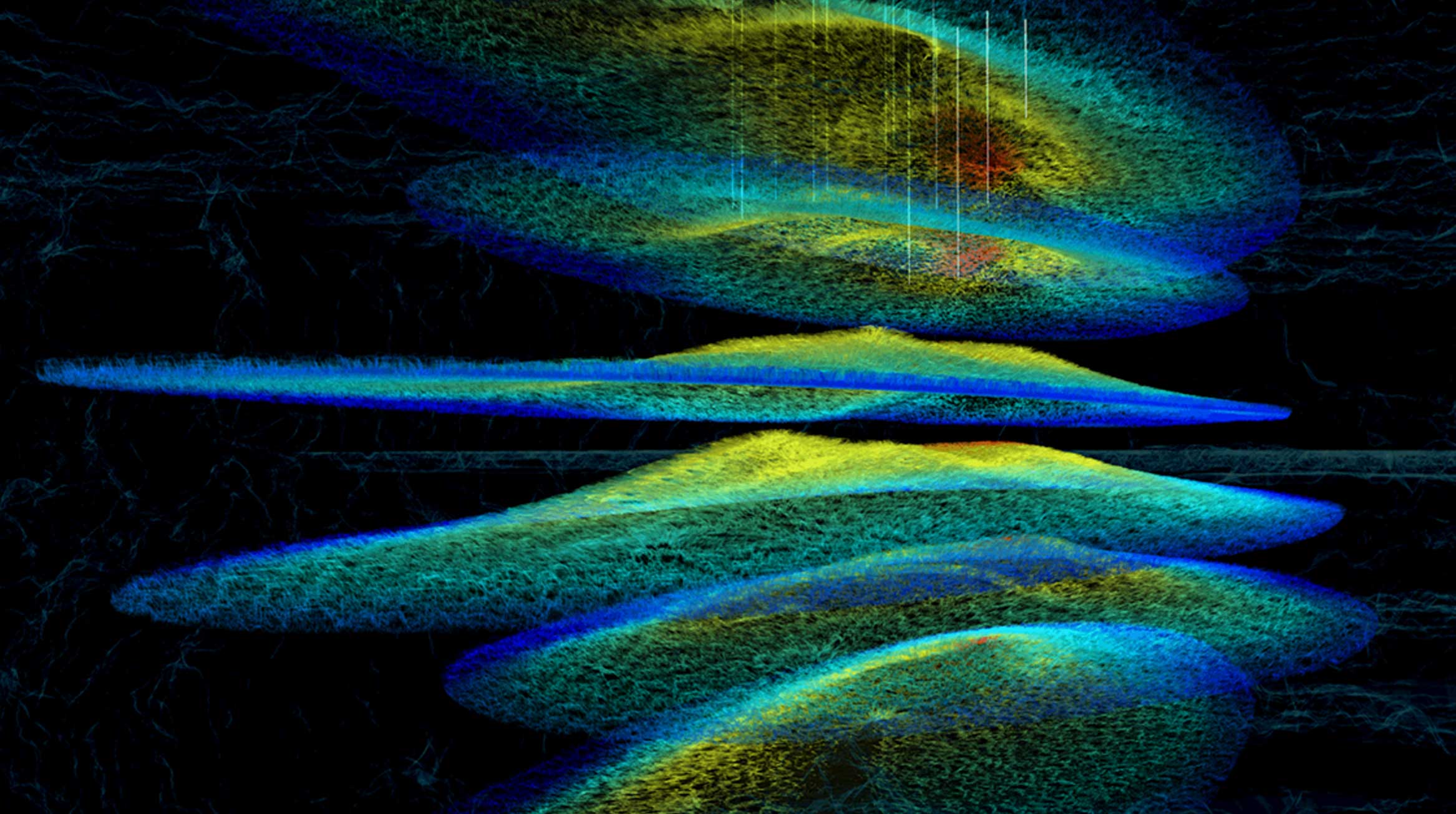
사우디 아람코는 마니파 저류층의 실시간 3D 프로파일을 생성하는 핵자기 공명 장치를 구축했다.
사우디 아람코는 유전뿐 아니라 사무실 공간에서도 혁신을 실현하며 사우디 아람코 공동체 내에서 '스마트 도시'를 건설하기 위해 사물 인터넷과 어드밴스드 애널리틱스를 활용하고 있다. 이러한 기술은 더 이상 미래지향적인 비전이 아니라 빠른 속도로 현실이 되고 있다. 예를 들어, 사우디 아람코의 통합 스마트 시티 시스템 프로젝트는 다란, 라스 타누라, 우다일리야, 아브다이크에 소재한 사우디 아람코의 주요 공동체에 적용될 예정이다. 이 프로젝트는 스마트 센서와 인공지능을 활용하여 스마트 가로등, 지능형 주차, 스마트 전력, 수도 계량기, 복합 운송을 모두 포함할 전망이다. 사우디 아람코의 목표는 물과 에너지를 절약하고 사우디 아람코 공동체의 삶의 질을 향상시키는 것이다.
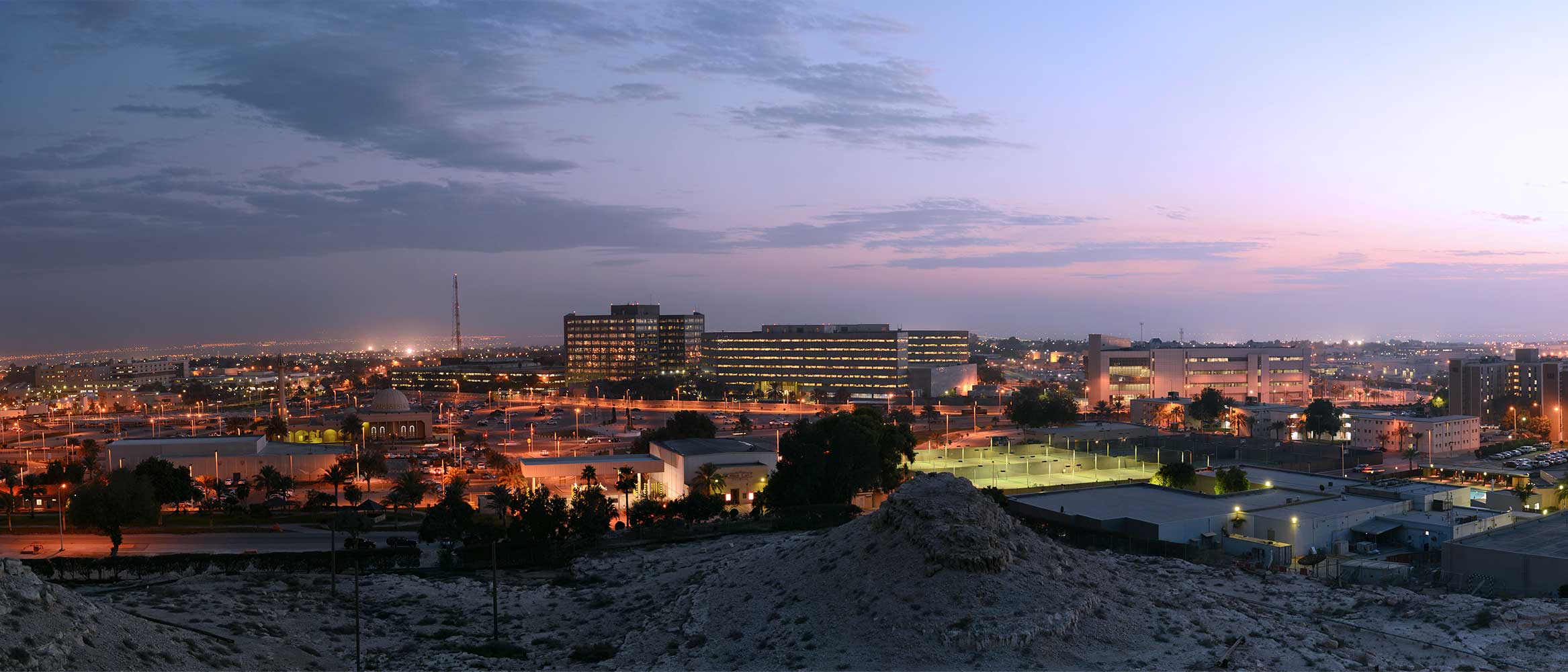

사우디 아람코는 다란에 위치한 사무실 공간에서도 사물인터넷(IoT)과 고급 분석 기술을 활용해 공동체 내 '스마트 도시' 구축을 추진하고 있다.
업스트림에서 다운스트림에 이르기까지 사우디 아람코는 이러한 기술적 혁신을 전면적으로 활용하기 위해 최선을 다하고 있다. 사우디 아람코의 최첨단 4차 산업혁명센터 (4IRC)는 이러한 혁신과 기술이 어우러지는 허브로 기능한다.
혁신의 등대
2,500m2가 넘는 규모의 4IRC는 에너지의 미래에 전념하고 있다. 기술의 본격적인 적용을 시작하기에 앞서 탐색, 아이디어 개발, 프로토타입 제작, 시범 프로젝트를 수행한다. 이곳에는 270m2의 비디오월이 설치되어 총 1억 900만개 이상의 픽셀이 다수의 클러스터와 존으로 분할되어 있는데, 그 중에는 20개가 넘는 운영 솔루션이 표시되는 AI 허브 (Artificial Intelligence Hub)의 거대한 커브드 스크린이 있다.







